The Nature of National Sovereignty, Territorial Integrity, International Peace, and Diplomacy
Source: 2022 Accomplishment Report Department of National Defense
Since the emergence of the modern nation-state system, the concept of state sovereignty has been a key principle of international relations, and intimately linked to territorial integrity. Territorial integrity essentially refers to the inviolability of the State’s physical territory and borders, whereas sovereignty is defined as the exclusive right of the State to exercise political power within its borders. These principles are critical in maintaining international order, that if these are not recognized or respected, and the delineation between states has been blurred, would result in chaos and instability. The Department of National Defense (DND), the country’s primary security institution, is mandated to protect and defend the country against threats that undermine the nation’s peace and security. Furthermore, in the exercise of its executive supervisory role over the Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP), the Department ensures that the latter’s primary mission of upholding the sovereignty, supporting the Constitution, and defending the territory of the Republic of the Philippines against all enemies, foreign and domestic, are always upheld.
The DND and the AFP’s primary responsibility in advancing the national interest of the State to maintain its sovereignty is through safeguarding and defending its territory by resisting external and internal threats. The measure of fulfilling its purposes is anchored on whether the Philippine territory is preserved from the consequences of external and internal aggressions towards the State, a functioning democracy with a government that is able to exercise full authority within its borders and without interference, and that the individual rights of the people within the state are kept. Over the years, the territorial and maritime disputes in the West Philippine Sea (WPS) have been one of the most prominent national issues and strategic priorities across administrations since the 1995 Mischief Reef incident. That for the past years, the Defense Department has been working towards an effective deterrence approach to preserve a peaceful status quo favorable to the nation, by gearing towards a Credible Defense Posture for the AFP through joint force development (JDF). In defending the Philippine territory, the Department undertakes various external defense operations to exercise and implement its programs on terrestrial domain, maritime territory, airspace, and cyberspace for the overall protection of the country’s national interests. These are realized through the expansion of Air and Surface Domain Awareness; conduct of Maritime Patrols (MARPAT); establishment of Effective Presence on Key Locations; Control over the Sea Lines of Communications; and Uphold and Harness Alliances and Strategic Partnerships. Significantly, all these are driven and complemented by the Department’s Capability Development and Modernization Programs.
In the context of territorial defense, a Credible Defense Posture is pursued purposely to prevent unauthorized entry and to deter any unlawful extraction of natural resources found within the country’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). The country’s integrated approach to territorial defense includes the use of government assets in increasing air and surface domain awareness, as well as the conduct of maritime patrols or MARPAT, which involves both aerial and maritime patrol operations. For CY 2022, the AFP continued to sustain the operational tempo of the country’s maritime and air defense with the conduct of 484 Air Patrols and 661 Surface Patrols across the WPS, Sulu-Celebes Seas, and other strategic areas for maritime concerns. MARPAT is a critical component of territorial security for nations around the world. The conduct of aerial and maritime patrols are essential for national defense, to secure borders and protect citizens, especially in areas with geopolitical tensions or territorial disputes. Especially with archipelagos, patrols serve as a visible deterrent to potential aggressors and help to ensure that borders are respected, and territorial integrity is maintained.
The Legal Basis of The Agency
Source: 2022 Accomplishment Report Department of National Defense
On 31 October 1939, President Manuel Luis Quezon issued Executive Order No. 230, formally creating the Department of National Defense (DND) on 01 November with the primary role of supervising the national defense program of the country. In the aftermath of the Second World War, the Department was re-established after it was merged with other departments during the war. During this time, it was given the additional task of assisting the government in promoting peace and law and order. In 1947, with an Executive Order. 94, s. 1947, DND was given executive supervision over the Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP). Years later, through the Administrative Code of 1987, the Government Arsenal (GA), National Defense College of the Philippines (NDCP) Office of Civil Defense (OCD), and Philippine Veterans Affairs Office (PVAO) joined the AFP in being under the supervision and control of the Department.
At present, the Department remains committed to its mission of defending the country against threats to its territorial integrity and sovereignty, and promote the welfare of the Filipino people to serve as one of the foundations for national development. In FY 2022, innovations were introduced to the Department and its bureaus, to assure the fulfillment of DND-wide priorities. In addition, with the wanning of the COVID-19 Pandemic, DND and its bureaus regained momentum on the projects that were restrained by the health emergency.
Sustained Efforts on the West Philippine Sea (WPS)
Source: 2022 Accomplishment Report Department of National Defense
Memorandum Circular No. 94, series 2016 created the National Task Force for the West
Philippine Sea (NTF-WPS) to “orchestrate and synchronize the employment of different national government agencies’ capabilities to achieve the national objectives in the WPS.” The DND is among the various government agencies that monitor the situation in the WPS and organize and institute whole-of-nation approaches, policies, and strategies to promote Philippine interests in the WPS. Through this mechanism, the Department remains a key player that contributes to the preservation and protection of the areas in the WPS where the Republic of the Philippines exercises sovereignty, sovereign rights, and jurisdiction, in accordance with the 1982 United Nation Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and the 2016 SCS Arbitration Award.
Towards a Self-Reliant Defense Posture
Source: 2022 Accomplishment Report Department of National Defense
Capability development can encompass a wide range of activities, such as enhancing military capabilities, capacity and readiness through the acquisition of new equipment and systems, the development of new tactics and strategies, and the training of personnel to fulfill force development objectives.
At the heart of the Department’s thrust to achieve a Credible Defense Posture is the acquisition of modern and advanced military assets. From a territorial defense perspective, capability developments enhance the country’s ability to detect, mitigate, and directly address threats. More importantly, its impact on establishing a strong and credible joint forces further contributes to integrated deterrence. Capability Development for the whole national defense apparatus is anchored on the 15-year modernization program that started in 2012 and will continue through 2027. The Republic Act (RA) 10349, also known as the Revised Armed Forces Modernization Act, was enacted to strengthen the AFP’s capability to address counterterrorism and internal threats. Over the years, the Department has reached milestones under Horizon 1, which looked to upgrade Internal Security Operations (ISO) and in performing Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Response (HADR) missions; and Horizon 2, which focused more on Territorial Defense through the acquisition of basic defense capabilities on land, sea, and air. Meanwhile, Horizon 3, the Project List which covers CYs 2023-2028, has been presented to the DND and AFP senior leaders, for deliberation and final endorsement/approval. By the end of 2022, the following big-ticket acquisitions were either negotiated, contracted, and completed:


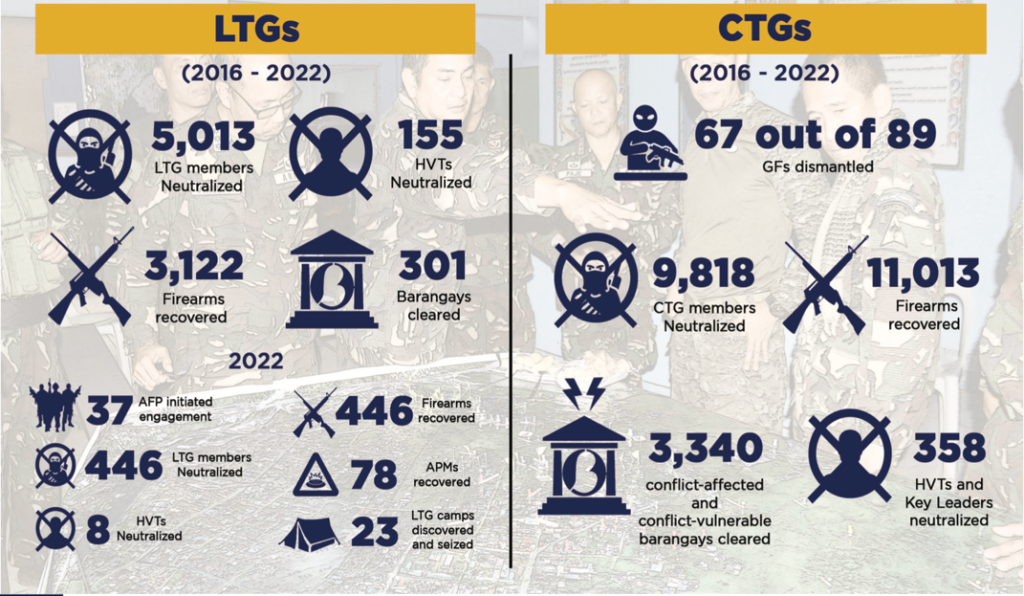
Securing the Nation
Sea-borne Kidnap-for-Ransom (KFR)
Highlighted by the continuous partnership with Indonesia and Malaysia under the 2016 INDOMALPHI Trilateral Cooperative Agreement (TCA), which facilitates the sharing of information and conduct of MARPAT through the Maritime Command Centers (MCCs). The TCA has been central in preventing kidnap-for-ransom incidents at sea in the past two years.
KFR INCIDENTS AT SEA (2016 - 2022)
No Data Found